How to repair Grub 2 Boot Loader on Ubuntu
On this page
Grub 2 was a long-awaited and very important upgrade over the previous version of the most popular and widely used boot manager in existence. Support for new filesystems, themes, improved splash capability, better internationalization, power-pc booting, dynamic module loading, and scripting support. All this is great, but things can still go wrong and break unexpectedly. This basically means that a bootable partition (operating system) may become inaccessible and this is why Grub v2 offers a powerful rescue mode. Now using this mode, may not be exactly a walk in the park for most inexperienced users out there, so here's a guide on how to easily fix your Grub with the Boot Repair tool.
Installing Boot Repair
Boot Repair is a simplistic but powerful enough tool that promises to repair the most frequent problems that may arise on a Grub installation. The tool is usually not available through the default repositories of most distributions out there, so users will have to install it from 3rd party repositories. One example that contains the latest version of the software (there are many others too) is the yannubuntu ppa. Ubuntu/Mint/ElementaryOS users may install this tool by typing the following commands on a terminal:
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:yannubuntu/boot-repair
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install boot-repair
Repair Grub 2 with Boot Repair
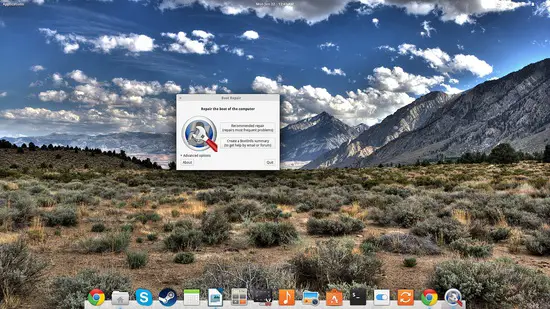
Upon launching the software, the tool detects your grub installation details and offers two main options that are: a.) standard repair (attempting to repair the most frequent problems by installing grub with default options), and b.) create a boot info summary (to provide input for when asking for help in forums etc).
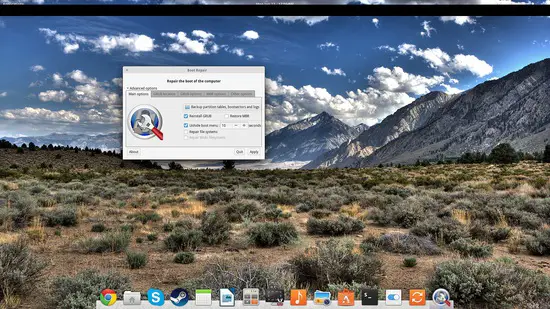
Besides those two main options, users may also press the “advanced options” menu which offers a set of more specialized settings and options. From there you may change the countdown duration, hiding of the menu, location of grub installation, and the default boot option/entry.
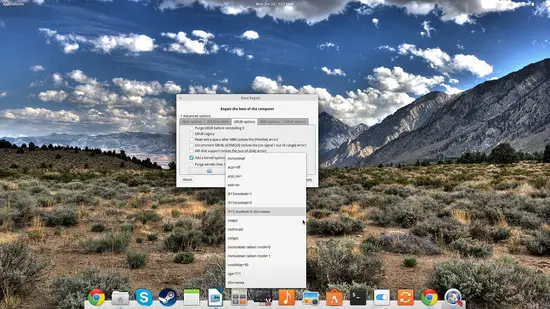
For even more specialized options, you may choose the “GRUB options” tab that contains problem-specific solution settings like for “no signal/out of range” error, or the “out of disk” error. The best part is the ease with which new kernel boot parameters can be added from this menu. All of the most commonly used additional parameters are included as options, as shown in the following screenshot.
It is important to note that Boot Repair is also available as a bootable ISO disk (live CD or live USB) (http://sourceforge.net/p/boot-repair-cd/home/Home/). There are many cases of broken Grub installations when these live images may come in handy, so keeping them in your drawer as proactive prevention of data and time loss is wise.
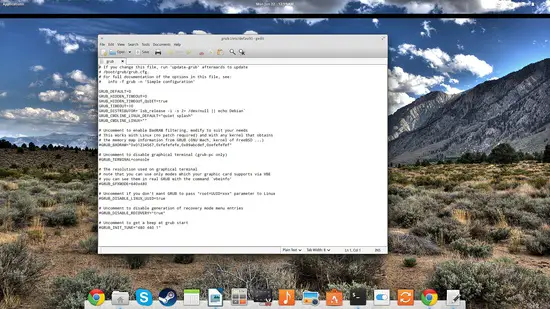
If all of the above fails, keep in mind that Grub 2.0 settings are stored in /etc/default/grub, so if you open it with a text editor as root, you will be able to edit the options and enable or disable the various settings. In this configuration file, you will find some options that are not available in Boot Repair, so knowing that what you do in the tool reflects here is important. For any changes to take effect, you should “Save” the file and run “update-grub” afterward to update the /boot/grub/grub.cfg file which is were Grub reads its settings from. Good luck!